Problem1 - d¶
Compare your results with different grid resolutions to evaluate the numerical error and the order of the scheme.
The qualitative comparison between different grid spacing for Re=100 case has been made in the previous section. As observed, the less grid point is, the less accurate and the more unstable solution were achieved. Please see section b.
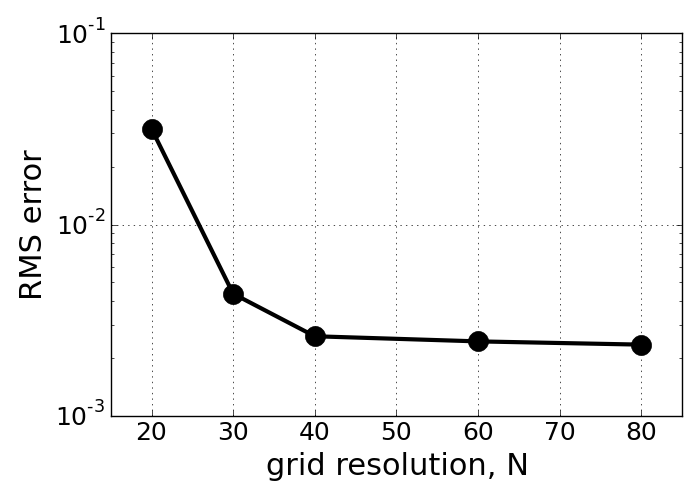
In order to evaluate the numerical accuracy, the numerically resolved LBM data is compared to the reference data in terms of u-velocity component along the centered axial location. Assuming the reference data to be target data that is achieved when the numerical data is accurate, the root mean square (RMS) values were evaluted from the different grid spacing setups.
Overall, the accurate solution can be achieved with finer grid spacing setup. It means again that the smaller grid size contributes to less numerical error. As stated in the previous section, smaller grid spacing is more favorable condition for LBM because original Boltzmann equation was derived in molecular scales of length and time and so it can be more reliable when it is employed in the small spaced lattice configuration.
In addition, the RMS error seems to be stablized as the grid resolution goes beyond 60 or more. Since the current Python script running for LBM is not such efficient, all the grid spacing analysis and fully resolved solution were discussed based on 60x60 resolution.