Problem1 - g¶
Compare the results obtained in homework 3,4, and 5. Discuss the advangates and disadvantages of the methods.
In this test, Re=100 case has been chosen for the desired comparison because this case doesn’t not require impractically higher grid resolution such that the test can be performed very efficiently. The selected grid resolution is 60x60 and three different solution methods were tested under the same condition. All the simulation for these solution methods were conducted with the same convergence rate of 0.01% for u-velocity residual.
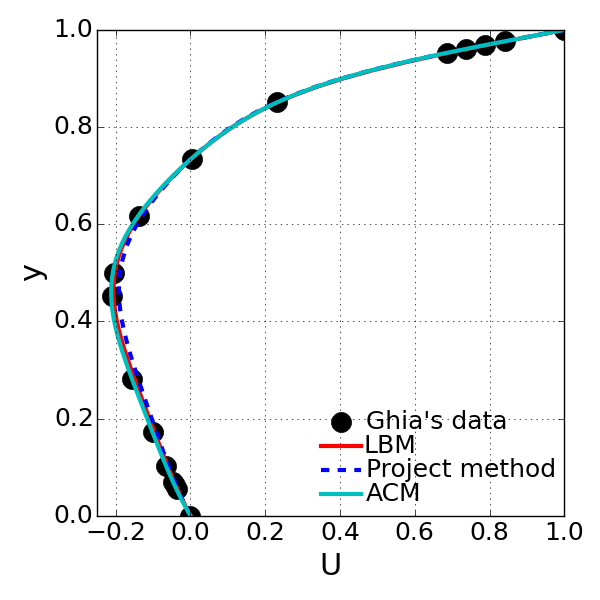
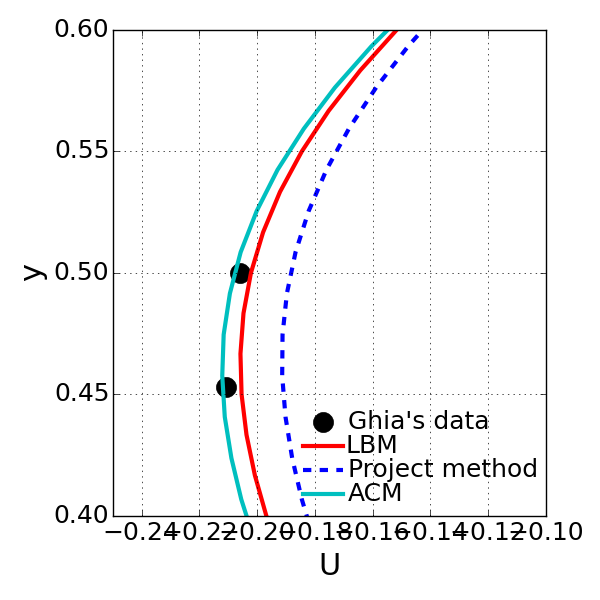
<Comparison on the calculated u-velocity along the centerline with different solution method: bottom image is the magnified one for noticing the discrepancy>
- Observations
- Overally all the solution methods were successfully running to achieve the reliable flow behaviors.
- However, there are noticeable discrepancy when there are compared to each other: Projection method is the worst at accuracy.
- It seems that more iterations may be needed to have accurate solution for Projection method.
- ACM gives the most accurate solution. However, in order to assess the solution method’s accuracy, further investigation needs to be done for reliable assessment.
LBM Projection method ACM RMS of u-velocity 0.00413982355618 0.00857537642521 0.00132103968968 Iterations for convergence 4889 3496 37017 Compute time for convergence 784.86 4145.3 1711.31
Above table describes the computational performance among different solution methods. Here the projection method again turns out to be worst case in terms of computational time. This is because the projection method is to solve Laplacian equation for pressure correction terms which is the most expensive part in the whole process. Given grid resolution, the projection method requires more than 150 iterations for SOR method in the pressure correction step.
On the otherhand, LBM was the best way to have accurate solution with less computational effort. However, this comparison may not be reliable because the computational time is also very strongly senstive to how the efficiently and effectively simulation code is made.